Deduction Database
Comprehensive tax deduction database to help you identify eligible deductions, maximize your tax savings, and stay compliant with IRS regulations. Browse our extensive collection of deduction resources.

Small Business Health Care Premium Credit: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Employers
The Small Business Health Care Premium Credit offers eligible employers a substantial tax incentive, providing up to 50% of healthcare premium costs. To qualify, businesses must enroll through the SHOP Marketplace, maintain fewer than 25 full-time equivalent employees, and ensure average annual wages remain below $56,000. This credit helps reduce operational expenses while promoting employee wellness, making it a vital consideration for small business tax strategy. Understanding eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and compliance requirements ensures optimal financial benefits and sustained organizational health.

Emergency Personal Expenses Distribution: Expanded IRS Penalty Exceptions
Effective January 1, 2024, the IRS has expanded exceptions to the 10% early withdrawal penalty for qualified retirement account distributions used for emergency personal expenses. This change, detailed in IRS Publication, allows individuals facing unforeseen financial hardships—such as medical emergencies, essential home repairs, or sudden unemployment—to access funds without incurring additional taxes. Key provisions include applicability to distributions after December 31, 2023, and specific eligibility criteria for emergency expenses. This update provides critical financial flexibility, helping taxpayers manage unexpected costs while remaining compliant with tax regulations. Always consult a financial advisor to assess individual circumstances.

Qualified Transportation Fringe Benefit: Maximizing Tax-Free Commuter Benefits
The Qualified Transportation Fringe Benefit allows employees to receive up to $300 per month in tax-free compensation for qualified commuting expenses, including transit passes, vanpooling, and parking. This employer-provided program reduces taxable income while promoting sustainable commuting. The IRS sets annual adjustments to these limits, with current provisions detailed in Publication 15-B. Employers must comply with substantiation requirements and non-discrimination rules, while employees benefit from reduced out-of-pocket costs and simplified expense tracking through payroll deductions.

Mortgage Interest Deduction: A Comprehensive Guide to Tax Benefits for Homeowners
The mortgage interest deduction enables homeowners to reduce their taxable income by deducting interest paid on mortgages for primary and second residences. Eligibility and limits depend on the home purchase date: properties acquired before December 15, 2017, qualify for deductions on up to $1,000,000 in acquisition debt, while those purchased after are limited to $750,000. To claim this deduction, taxpayers must be legally obligated on the loan and provide lender-reported payment documentation. Understanding these rules helps maximize tax savings and ensure IRS compliance.

Premium Tax Credit: Reducing Health Insurance Premium Costs
The Premium Tax Credit (PTC) is a refundable tax credit designed to assist eligible individuals and families in affording health insurance premiums purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace. It targets those with household incomes between 100% and 400% of the federal poverty level, allowing advance payments to insurers or claims on tax returns. Even non-filers can benefit, provided they meet IRS criteria. This credit helps reduce out-of-pocket premium expenses, promoting accessible healthcare coverage under the Affordable Care Act.

Charitable Contribution Deduction: A Comprehensive Guide to Itemized Tax Benefits
The charitable contribution deduction enables taxpayers who itemize to reduce their taxable income by donating cash or property to IRS-qualified nonprofit organizations. This incentive supports philanthropy while offering financial relief, requiring proper documentation like receipts and adherence to annual deduction limits. Eligible contributions range from monetary gifts to appreciated assets, with specific rules for non-cash items such as stocks or vehicles. Understanding eligibility criteria, record-keeping standards, and filing procedures ensures compliance and maximizes tax savings, making it essential for strategic financial planning.
Student Loan Interest Deduction: Maximize Your Tax Benefits
The Student Loan Interest Deduction is an above-the-line tax deduction allowing eligible taxpayers to deduct up to $2,500 annually in qualified student loan interest payments. This deduction does not require itemization, making it accessible to all qualifying filers. Eligibility phases out for single filers with modified adjusted gross incomes exceeding $80,000 and joint filers over $165,000. This guide details qualification criteria, calculation methods, and strategic approaches to optimize this valuable tax benefit while ensuring compliance with IRS regulations.

Work Opportunity Tax Credit
The Work Opportunity Tax Credit (WOTC) is a federal tax incentive designed to encourage employers to hire individuals from specific target groups who face significant barriers to employment. Administered by the IRS, this credit provides financial benefits to businesses that hire veterans, ex-felons, long-term unemployed individuals, and other eligible groups. By reducing tax liability, the WOTC supports workforce diversity and economic inclusion while helping employers lower their overall employment costs. Proper documentation through Form 3800 is essential for claiming this credit, which can significantly impact a company's bottom line and community engagement efforts.

Self-Employed Health Insurance Deduction: Maximize Tax Savings with Form 7206
Self-employed individuals can deduct health insurance premiums for themselves, spouses, and dependents through Form 7206, reported on Schedule 1 (Form 1040), line 17. Eligible premiums include medical, dental, and long-term care insurance, offering substantial tax relief by reducing adjusted gross income. Key requirements include having net earnings from self-employment and not being eligible for employer-sponsored health plans. This deduction can lower tax liability by up to 37% of premium costs, depending on the taxpayer's bracket, and applies to various self-employment structures like sole proprietorships and partnerships. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines ensure compliance and maximize benefits.

Family and Medical Leave (FMLA) Tax Credit: Eligibility, Calculations, and Strategic Benefits for Employers
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Tax Credit offers eligible employers a significant financial incentive, providing a tax credit ranging from 12.5% to 25% of wages paid to employees on FMLA leave. To qualify, employers must meet specific criteria outlined by the IRS, including maintaining compliant leave policies and ensuring wage replacement rates are at least 50%. This credit, claimed via Form 8994, helps offset the costs of providing paid family and medical leave, supporting workforce stability and compliance with federal regulations. Proper documentation and adherence to eligibility requirements are essential for maximizing this benefit.

Qualified Charitable Distribution: Maximizing Tax Benefits Through IRA Giving
A Qualified Charitable Distribution (QCD) allows individuals aged 70½ or older to transfer up to $100,000 annually directly from an IRA to qualified charities, counting toward Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) without being included in taxable income. Starting in 2023, a one-time election permits up to $50,000 to be distributed to charitable remainder unitrusts or charitable gift annuities, offering lifetime income streams while supporting charitable causes. This strategy reduces adjusted gross income, potentially lowering taxes on Social Security benefits and Medicare premiums. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines are essential for compliance.
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): Maximizing Your Refund
The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is a significant refundable tax credit designed to assist low- to moderate-income workers and families. By reducing tax liability and potentially providing refunds exceeding taxes paid, it supports financial stability. Eligibility hinges on earned income, filing status, and the number of qualifying children, with credit amounts scaling based on these factors. Administered by the IRS, the EITC can deliver substantial financial benefits, making it essential for eligible taxpayers to understand and claim it accurately to enhance their tax outcomes.

Employee Retention Credit: A Comprehensive Guide for COVID-19 Impacted Businesses
The Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a refundable tax credit designed for employers who continued to pay employees during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eligible businesses and tax-exempt organizations can claim up to $26,000 per employee through 2024 using Form 941. Qualification criteria include full or partial suspension of operations or significant declines in gross receipts. This guide covers eligibility requirements, calculation methods, application procedures, and strategic considerations for maximizing this financial relief opportunity while maintaining compliance with IRS regulations.

Coverdell Education Savings Account
Coverdell ESAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts designed to help families fund K-12 and higher education expenses. With an annual contribution limit of $2,000 per beneficiary, these accounts allow tax-free growth and withdrawals for qualified educational costs, including tuition, books, and supplies. While contributions are not tax-deductible, the accounts offer significant long-term savings benefits, particularly for elementary and secondary education expenses not covered by 529 plans. Income phase-outs apply, making them most beneficial for moderate-income households seeking flexible education funding solutions.
Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit: Maximizing Innovation Incentives
The Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credit offers businesses a substantial incentive to invest in innovation, covering up to 20% of qualifying R&D expenses. This credit targets activities that advance technology, improve products, or enhance processes, directly reducing tax liability and encouraging sustained investment in research. Eligible expenses include wages, supplies, and contracted research costs. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines are essential to claim this credit, which can significantly lower a company's tax burden while fostering long-term growth and competitiveness in the market.

2024 Retirement Plan Contribution Limits: Maximizing Your Tax-Advantaged Savings
The IRS has announced significant updates to retirement plan contribution limits for 2024, allowing individuals to contribute up to $23,000 to 401(k), 403(b), and Thrift Savings Plans. Those aged 50 and older can make additional catch-up contributions of $7,500, bringing their total potential contribution to $30,500. These increased limits provide substantial opportunities for tax-deferred growth and immediate tax savings. Understanding these limits is crucial for effective retirement planning and tax strategy optimization, particularly for high-income earners seeking to maximize their retirement savings while reducing current tax liabilities.

Health Savings Account (HSA) Contribution Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits in 2024
The Health Savings Account (HSA) contribution deduction enables eligible individuals to reduce their taxable income through pre-tax or tax-deductible contributions to an HSA, provided they are enrolled in a qualifying high-deductible health plan (HDHP). For the 2024 tax year, the IRS has increased contribution limits, allowing single coverage holders to contribute up to $4,150 and family coverage holders up to $8,300, with an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution for those aged 55 and older. This above-the-line deduction not only lowers your adjusted gross income but also supports long-term healthcare savings with tax-free growth and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.

2024 Standard Deduction: Complete Guide to Tax Savings
The Standard Deduction for 2024 is a fundamental tax provision allowing single filers to deduct $14,600 and married couples filing jointly to deduct $29,200 from their adjusted gross income, reducing taxable income without itemizing expenses. Annually adjusted for inflation, this deduction simplifies tax filing and lowers tax liability for millions. Key aspects include automatic application, filing status variations, and specific rules for dependents, making it essential for efficient tax planning and compliance with IRS guidelines.

Traditional IRA Contribution Deduction: Maximizing Your 2024 Tax Benefits
The traditional IRA contribution deduction allows eligible taxpayers to reduce their taxable income by contributing to a traditional IRA. For the 2024 tax year, individuals can deduct up to $7,000 ($8,000 if age 50 or older). Deduction eligibility is subject to phase-out rules based on modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) and whether you or your spouse are covered by a workplace retirement plan. Understanding these rules is crucial for optimizing tax savings and retirement planning strategies.
Domestic Abuse Distribution Exception: Waiving the 10% Early Withdrawal Penalty
The Domestic Abuse Distribution Exception, effective for distributions made after December 31, 2023, exempts eligible domestic abuse victims from the 10% additional tax on early withdrawals from qualified retirement plans. This provision, detailed in IRS guidelines, offers crucial financial relief by allowing penalty-free access to funds during times of crisis. To qualify, distributions must meet specific requirements, including verification of abuse and adherence to annual limits. This exception supports victims in achieving financial independence without the burden of early withdrawal penalties, aligning with broader efforts to provide compassionate tax solutions.

2024 Standard Deduction: Complete Guide to Increased Amounts and Tax Savings
The Internal Revenue Service has announced significant increases to the standard deduction for the 2024 tax year, providing taxpayers with enhanced tax-saving opportunities. Single filers and married individuals filing separately will benefit from a $14,600 deduction, while married couples filing jointly can claim $29,200. Heads of household receive a substantial $22,500 standard deduction. These adjustments represent approximately 5% increases from 2023 levels, reflecting ongoing inflation adjustments. Understanding these changes is crucial for optimizing tax strategies and maximizing potential refunds while maintaining compliance with current tax regulations.

Medical Expense Deduction: Maximizing Tax Savings on Healthcare Costs
The medical expense deduction allows taxpayers to reduce taxable income by deducting qualified medical and dental expenses exceeding 7.5% of their adjusted gross income (AGI). Eligible expenses include health insurance premiums, out-of-pocket costs for treatments, prescriptions, and preventive care. This guide details calculation methods, documentation requirements, and strategic planning to optimize deductions while ensuring IRS compliance, helping individuals manage healthcare expenses effectively and lower their overall tax liability.
Qualified Vehicle Interest Deduction: Maximize Tax Benefits for Personal Auto Loans (2025-2028)
The Qualified Vehicle Interest Deduction, effective from 2025 through 2028 under the IRS One Big Beautiful Bill Act, allows eligible taxpayers to deduct interest paid on loans for qualifying personal vehicles. With a maximum annual deduction of $10,000, this benefit phases out for single filers with modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) over $100,000 and joint filers exceeding $200,000. To qualify, vehicles must be new with original use commencing with the taxpayer and cannot include business or commercial vehicles. This guide details eligibility criteria, calculation methods, phase-out mechanics, and strategic tips to optimize your tax savings while remaining compliant with IRS regulations.

IRA Contribution Limits for 2024: Complete Guide with Deduction Rules
For 2024, the standard IRA contribution limit is $7,000, with an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution available for individuals aged 50 and older, making the total limit $8,000 for eligible savers. However, tax deductions for these contributions may be phased out based on modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) and participation in employer-sponsored retirement plans. This guide covers detailed eligibility criteria, income phase-out ranges, contribution deadlines, and strategies to maximize tax advantages while staying compliant with IRS regulations outlined in Publication 505.
Adoption Credit
The adoption credit for 2025 provides a maximum benefit of $17,280 for qualified adoption expenses, offering significant tax relief to eligible taxpayers. To qualify, your modified adjusted gross income must be below $299,190, and the credit can be claimed for both domestic and international adoptions. This comprehensive guide covers eligibility criteria, calculation methods, documentation requirements, and strategic planning tips to maximize your tax savings while ensuring compliance with IRS regulations outlined in Publication 505.

Senior Additional Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Individuals 65 and Older
The Senior Additional Deduction, effective from tax years 2025 through 2028, provides eligible individuals aged 65 and older with an extra $6,000 deduction to reduce taxable income. Married couples filing jointly may claim up to $12,000 if both spouses qualify. This deduction supplements existing senior tax benefits, offering substantial savings and strategic financial planning opportunities. Understanding eligibility criteria, claiming procedures, and integration with other deductions is essential for optimizing tax outcomes during these years.
Clean Vehicle Tax Credit: Maximize Your 2023 Tax Savings
The Clean Vehicle Tax Credit offers up to $7,500 for qualifying new plug-in electric or fuel cell vehicles purchased in 2023. This comprehensive guide details eligibility requirements, including North American manufacturing, income limits (up to $300,000 for joint filers), and vehicle-specific criteria. Learn how to claim this credit, understand phase-out thresholds, and integrate it with other tax strategies to optimize your financial benefits while supporting sustainable transportation.

Health Savings Account (HSA) Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits with Qualified Contributions
The Health Savings Account (HSA) deduction allows eligible taxpayers to deduct contributions made to their HSA, directly reducing taxable income. To qualify, individuals must be covered by a high-deductible health plan (HDHP), with 2024 limits set at $4,150 for self-only and $8,300 for family coverage. Contributions grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are not taxed. This guide details eligibility requirements, contribution strategies, IRS guidelines, and how HSAs compare to other tax-advantaged accounts, helping you optimize savings while complying with tax laws.
Fringe Benefits Tax Limit: Understanding the $300 Monthly Cap on Qualified Transportation and Parking Benefits
The IRS has increased the monthly limit for tax-free qualified transportation and parking fringe benefits to $300 in 2023, up from $280 in 2022. Employers can provide these benefits—covering transit passes, vanpooling, and parking—without incurring additional tax liabilities for employees. This adjustment reflects inflation and aims to support commuting expenses. Understanding these limits helps both employers structure compliant benefit programs and employees maximize tax-free compensation. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines are essential to avoid penalties.

Home Office Deduction: A Complete Guide for Self-Employed and Remote Workers
The home office deduction allows self-employed individuals and remote workers to deduct expenses for a workspace used regularly and exclusively for business. Eligible costs include portions of rent, utilities, real estate taxes, repairs, and maintenance, calculated based on the business-use area of the home. Proper documentation and adherence to IRS guidelines are essential to claim this deduction accurately and avoid audits. This guide covers eligibility, calculation methods, and common pitfalls to help you maximize tax savings.

Home Mortgage Interest Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Homeowners
The Home Mortgage Interest Deduction allows homeowners to deduct interest paid on up to $750,000 of acquisition debt for first and second homes purchased after December 15, 2017. Special provisions protect pre-2017 mortgages from the new limit if refinancing does not increase the original loan amount. This comprehensive guide details eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and strategic approaches to optimize deductions while maintaining IRS compliance. Understanding these rules can significantly reduce taxable income and enhance long-term financial planning for residential property owners.

Individual Retirement Account (IRA) Deductions: 2024 Limits and Tax Strategies
For 2024, IRA deductions allow individuals under 50 to contribute up to $7,000 and those 50 and older up to $8,000, directly reducing taxable income. These deductions are subject to modified adjusted gross income (AGI) phase-outs, particularly for individuals covered by workplace retirement plans. Married couples filing jointly begin phase-outs at $230,000 AGI, with deductions completely phased out at $240,000. Contributions must be made by the tax filing deadline, typically April 15 of the following year, offering a strategic tax-saving approach for retirement planning. Always consult IRS Publication 17 or a tax professional for personalized guidance.

Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT): Comprehensive Guide to Calculation, Impact, and Strategic Planning
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) represents a parallel federal income tax system designed to ensure high-income taxpayers pay a minimum amount of tax regardless of deductions, credits, or exemptions. Created through the Tax Reform Act of 1969, AMT requires taxpayers to calculate their liability twice—once under regular income tax rules and again under AMT provisions—then pay the higher amount. This comprehensive guide explores AMT mechanics, exemption amounts, applicable tax rates, common triggers, calculation methodologies, and strategic approaches to minimize AMT exposure while maintaining compliance with IRS regulations.
Overtime Compensation Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Extra Hours Worked
The Overtime Compensation Deduction, effective from 2025 to 2028 under the IRS One Big Beautiful Bill Act, enables eligible taxpayers to deduct qualified overtime pay exceeding their regular rate. Individual filers can claim up to $12,500 annually, while joint filers are eligible for up to $25,000, subject to phase-out thresholds starting at $150,000 modified AGI for individuals and $300,000 for joint filers. This deduction targets wage earners seeking to reduce taxable income through documented overtime, offering substantial savings for those managing increased work hours. Consult a tax advisor to ensure compliance and optimal benefit utilization.

Foreign Earned Income Exclusion: Maximizing Tax Benefits for International Earners
The Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE) allows qualifying U.S. taxpayers to exclude up to $120,000 of foreign-earned income from their 2023 federal tax returns. This provision applies specifically to income earned outside the United States and requires meeting either the Bona Fide Residence Test or Physical Presence Test. Properly utilizing the FEIE can significantly reduce overall tax liability for expatriates and international workers while maintaining compliance with IRS regulations. Understanding eligibility requirements, calculation methods, and filing procedures is essential for maximizing this valuable tax benefit.

2023 Gift Tax Exclusion: A Comprehensive Guide to $17,000 Annual Gifting Limit
The annual gift tax exclusion for 2023 allows individuals to gift up to $17,000 per recipient without incurring federal gift tax or filing requirements. This inflation-adjusted amount provides significant opportunities for tax-efficient wealth transfer and financial planning. Understanding the per-recipient application, exclusion mechanics, and strategic implications helps taxpayers optimize gifting strategies while maintaining compliance with IRS regulations. This guide covers exclusion specifications, detailed reporting thresholds, and practical applications for personal financial management.

Retirement Account Contributions: Maximizing Tax Deductions and Credits
Learn how contributing to retirement accounts such as IRAs, 401(k)s, SEP IRAs, and SIMPLE IRAs can reduce your taxable income and qualify you for valuable tax credits. This guide covers contribution limits, eligibility requirements, and strategies for optimizing deductions, including the Saver's Credit for low-income taxpayers, to enhance your retirement savings and tax efficiency.
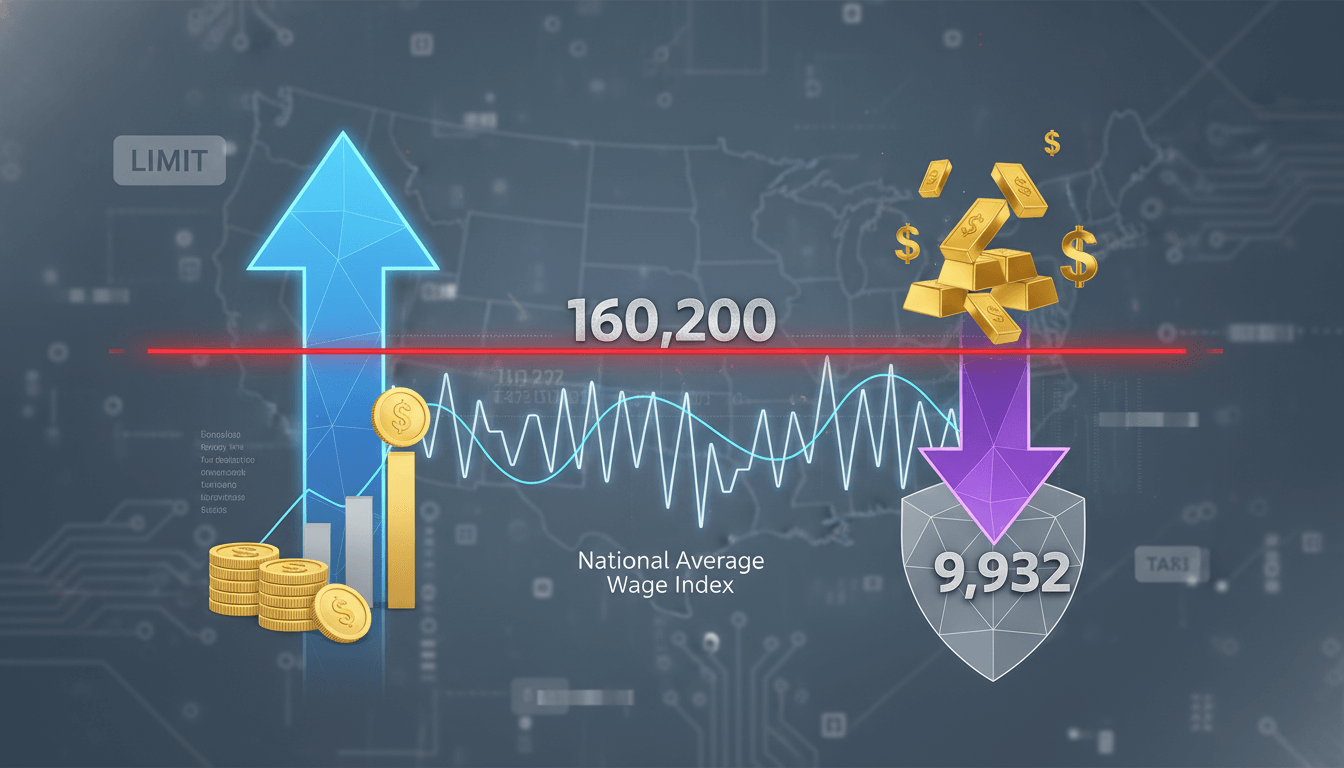
Social Security Tax Limit 2023: Maximum Earnings and Tax Withholding
The Social Security tax limit for 2023 sets the maximum earnings subject to payroll tax at $160,200, with a corresponding maximum annual tax withholding of $9,932. This annual adjustment, tied to the National Average Wage Index, ensures the system's sustainability. High-income earners benefit from this cap, as earnings above this threshold are not subject to Social Security tax. Understanding this limit is essential for accurate tax planning, payroll compliance, and optimizing personal financial strategies, especially for those with multiple income sources or self-employment income.
Standard Deduction Overview: 2025 Tax Year Guide
The standard deduction is a fundamental tax provision that allows taxpayers to reduce their taxable income by a fixed amount, determined by filing status. For the 2025 tax year, single filers can deduct $15,000, married couples filing jointly $30,000, and heads of household $22,500. Additional amounts are available for seniors aged 65 and older, enhancing tax savings. Approximately 89% of taxpayers opt for the standard deduction due to its simplicity and efficiency compared to itemizing. This guide explores eligibility, calculations, and strategic considerations to maximize your tax benefits.

Educator Expense Deduction: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Teachers
The Educator Expense Deduction allows eligible educators to deduct up to $300 for classroom supplies, with married joint filers potentially deducting up to $600. This above-the-line deduction reduces adjusted gross income, helping offset out-of-pocket expenses for materials like books, supplies, and equipment used in K-12 education. To qualify, educators must work at least 900 hours per academic year in a school providing elementary or secondary education. Proper documentation and understanding of eligible expenses are crucial for maximizing this tax benefit while maintaining compliance with IRS regulations.

State and Local Tax (SALT) Deductions: Limits, Eligibility, and Strategic Tax Planning
The State and Local Tax (SALT) deduction allows taxpayers to deduct up to $10,000 ($5,000 if married filing separately) for state and local income taxes, property taxes, and general sales taxes. This comprehensive guide covers deductible tax types, eligibility criteria, calculation methods, and strategic considerations for taxpayers in high-tax states. Understanding SALT limitations is crucial for accurate tax filing and optimizing overall tax liability under current IRS regulations.
Charitable Contribution Deductions: Maximizing Tax Benefits for Giving
Charitable contribution deductions allow taxpayers who itemize to reduce taxable income through cash and non-cash donations to qualified nonprofits. Essential requirements include maintaining documentation for gifts exceeding $250 and filing Form 8283 for non-cash contributions over $500. New provisions effective 2026 permit single filers to deduct up to $1,000 and married couples filing jointly up to $2,000 in cash donations without itemizing. This guide details eligibility, documentation standards, valuation methods, and strategic planning to optimize tax savings while supporting charitable causes.
